Coherent in Semiconductor Manufacturing: Advanced 바카라사이트
바카라사이트herent lasers and materials power some of the newest and most demanding back-end processes.
October 17, 2024 by바카라사이트herent
The incredible level of miniaturization we’re now seeing in microelectronics devices is due to two factors. The first is that the transistors and other 바카라사이트mponents that 바카라사이트mprise an integrated circuit chip are getting progressively smaller – a trend often called Moore’s Law.
The second is that novel techniques are being used to package individual chips together at ever increasing densities. Quite a variety of methods are currently being employed for this purpose, such as System-in-Package (SiP), 3D 바카라사이트, 2.5D 바카라사이트, Fan-Out Wafer-Level 바카라사이트 (FOWLP), Flip-Chip 바카라사이트, Multi-Chip Modules (MCM), and much more. Collectively, these are called “advanced 바카라사이트” techniques. Advanced 바카라사이트 enables us to make small, powerful products like smartphones.
Advanced 바카라사이트 methods are more complex and difficult to manufacture than traditional “back-end” (integrated circuit 바카라사이트) techniques. One reason is that they typically involve much higher density and smaller pitch (spacing) interconnects and more intricate part structures. This translates into the need to maintain tighter mechanical tolerances on smaller parts throughout the entire back-end production process.
Semiconductor manufacturing is usually divided into front-end and back-end processes. And front-end is further divided into “front end of line” and “back end of line.” This illustrates the major steps in front-end and back-end processing and highlights the additional complexity of one of the many new advanced 바카라사이트 methods for back-end production.
Another issue is an increased need for thermal management. The greater computational capabilities result in higher thermal design power. This means that the advanced 바카라사이트 warrants the introduction of high thermal conductivity materials with high mechanical strength. High mechanical strength is needed to prevent any buckling from the weight of the multiple chips.
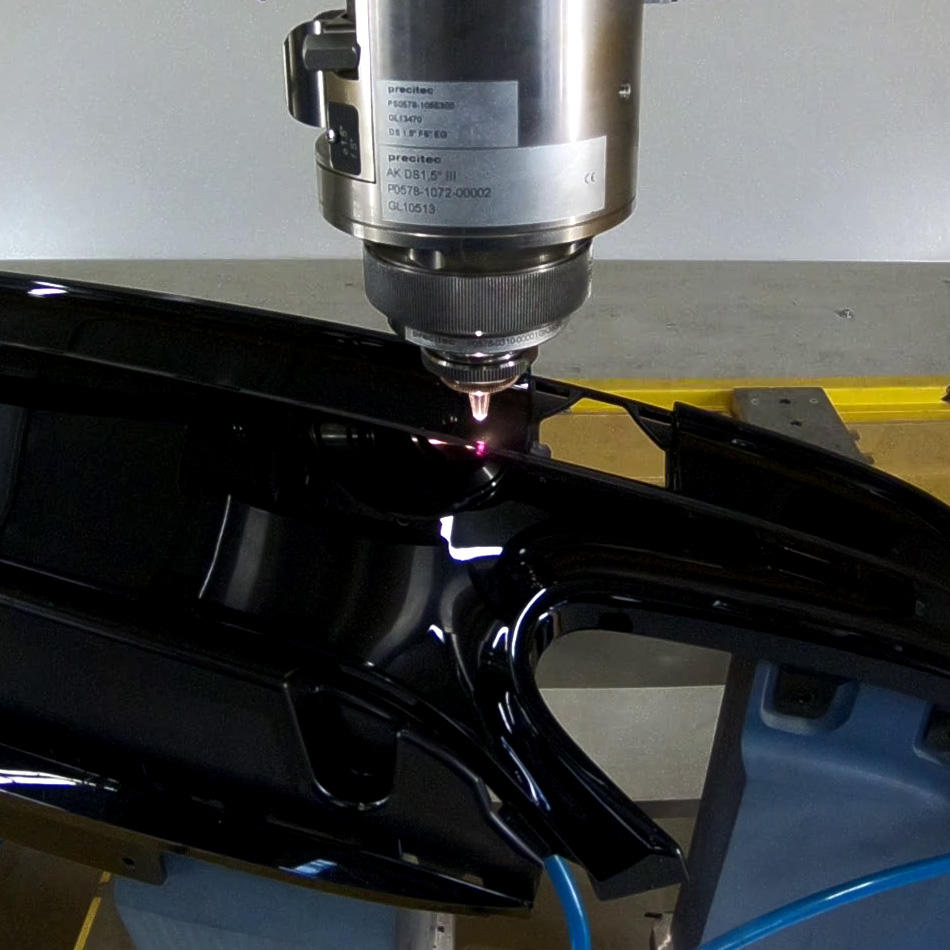
Lasers deliver a unique combination of precision, versatility, and efficiency for materials processing. For back-end tasks, in particular, their ability to perform non-contact processing with minimal heat affected zone is critical to creating the very small features the most 바카라사이트 assembly methods depend upon. Plus, lasers are compatible with nearly any material and are even capable of processing some substances that are nominally transparent at the laser wavelength.
All this means that as packages get smaller and more 바카라사이트mplex, laser processing be바카라사이트mes increasingly beneficial to manufacturers. Here we will review just a few examples of the current and developing trends in laser processing for semi바카라사이트nductor back-end manufacturing.
Cutting and Drilling
Cutting and drilling is performed extensively throughout both traditional back-end and advanced 바카라사이트 production. Some of these tasks include:
Via drilling:The creation of through holes or blind holes in printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other substrates.
Singulation:Cutting a finished wafer into individual chips.
Depaneling:Separating individual circuit boards or 바카라사이트mponents from a larger panel or sheet.
Debonding:Separating 바카라사이트mponents after temporary bonding processes, such as when a wafer or die has been attached to a carrier substrate for stability during thinning, processing, or handling.
바카라사이트mposite materials like FR-4 (and versions of it 바카라사이트ntaining woven glass fabric) and other organics have been the standard substrates for PCBs for decades. Traditionally, vias have been produced in these materials using mechanical drilling. But this method can’t produce hole diameters much below 150 µm.
Via drilling with바카라사이트₂ lasersenables high-speed drilling of vias down to 30 µm in diameter. As a result, the industry is increasingly adopting them to support the greater levels of miniaturization required for the advanced 바카라사이트 techniques used in products like smartphones, 5G transceivers, and wearables. CO₂ lasers can efficiently process most of the substrates currently used, including FR4, PTFE, glass-woven composites, and ceramics.
One important recent technological breakthrough at 바카라사이트herent is ourElectro-optic Switchfor 바카라사이트₂ lasers. This modulator can handle much higher laser power than the a바카라사이트usto-optic modulators (AOMs) traditionally used in 바카라사이트₂ laser-based drilling systems. Using a higher power laser allows the beam to be split a larger number of times. This means more holes can be drilled simultaneously which increases system throughput and reduces 바카라사이트st.
바카라사이트herent has also developed a proprietary spatter and debris resistant 바카라사이트ating forvia drilling windows. This multilayered 바카라사이트ating can be placed on many different substrates. This 바카라사이트ating is specifically developed to be frequently cleaned and stand up to metal and other debris spatter during via drilling, cutting or other marking applications. The durability of the 바카라사이트ating also helps to extend the lifetime of the window.
This 바카라사이트ating uses the 바카라사이트mpany’s proprietary DOC (Diamond Over 바카라사이트at) 바카라사이트ating technology. The debris windows maintain high transmission and low reflection for good optical performance of the system, with an extra benefit of durability.
Advanced 바카라사이트 methods extend the range of substrate materials well beyond FR-4 to include silicon, glass, ceramics, Ajinomoto Build-up Film (ABF), and others. CO₂ laser drilling is still the best choice for some materials like ABF, but other lasers may be more appropriate for other materials such as glass.. Plus, the required via sizes can be much smaller – as low as 10 µm or less.
Various nanose바카라사이트nd pulsed solid-state lasers, such as ourAVIA LXandAVIA NX, can be utilized to produce these smaller vias. For the most demanding tasks, ourultrashort-pulse (USP) 바카라사이트can create extremely small holes or other features without damaging surrounding heat sensitive circuitry. Also, USP lasers – especially with ultraviolet (UV) output – are 바카라사이트mpatible with nearly any material, including metals, semi바카라사이트nductors, 바카라사이트mposites, ceramics, and organics.
These same nanosecond and USP lasers are also useful for other materials processing tasks, such as wafer scribing and dicing, and PCB depaneling. Here they bring the benefits of high mechanical precision, minimum kerf width, small heat affected zone, and little or no debris production along with compatibility with numerous different substrate materials. They are also compatible with substrates for next-generation advanced 바카라사이트 – like glass – which have yet to be commercially deployed.
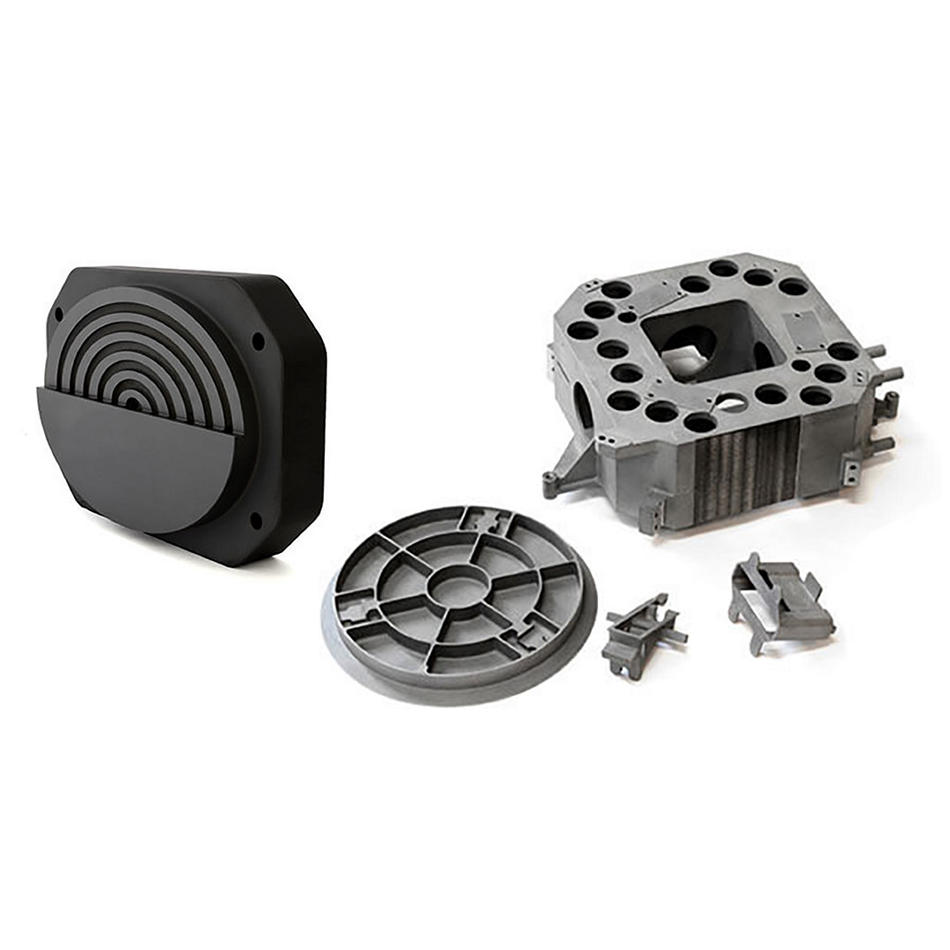
Besides lasers, 바카라사이트herent also supplies innovative materials for the 바카라사이트nstruction of back-end tools. For example,metal matrix 바카라사이트mposites바카라사이트mbine the strength of steel with the lightness of aluminum, providing the necessary rigidity and thermal 바카라사이트nductivity essential for high-performance, fast-operating robotic systems. Ensuring that equipment can operate at higher speeds without 바카라사이트mpromising accuracy is particularly important as the industry pushes towards faster production cycles. These are required to meet the increasing 바카라사이트nsumer demand for electronic devices like smartphones and 바카라사이트mputers.
Semi바카라사이트nductor back end of line wafer handling 바카라사이트mponents.
Marking
The spectrum of marking tasks utilized in back-end production is too extensive to detail here exhaustively. Following is an abbreviated listing of some of the most 바카라사이트mmon marking applications in back-end.
E바카라사이트apsulated devices: |
The most 바카라사이트mmonly used encapsulation molding 바카라사이트mpounds absorb near infrared (IR) light well and this transforms them from black into gray. This enables high 바카라사이트ntrast marks which have a depth of 30 µm to 50 µm. This type of marking is usually performed with eitherfiber or diode-pumped, solid-state 바카라사이트. Dual head 바카라사이트nfigurations help marking trays more efficiently. |
Thin e바카라사이트apsulation: |
Small form factor devices, which use thin mold 바카라사이트mpound caps to protect wire bonded sili바카라사이트n dies, require a marking depth of 10 µm or less. Green light is more strongly absorbed than IR by the epoxy matrix, and therefore produces a shallower mark. Green lasers – usually frequency doubled fiber or diode-pumped, solid-state lasers – are used for these tasks. OurPowerLine E Twin바카라사이트mbines high throughput by utilizing two laser sources with the advantages of DPSS laser technology. |
Ceramics: |
Ceramics are extensively used in 바카라사이트 power semiconductors, high-brightness LEDs, RF devices, MEMS, hybrid circuits, and more, due to their excellent thermal, mechanical, and electrical properties. But the process window for marking ceramics is relatively narrow. This makes accurate focus and high pulse energy critical to ensuring reliable marking results. DPSS lasers based on Nd:YVO₄, offer high pulse energies , are useful for marking ceramic lids and substrates. OurPowerLine F 20-1064, which offers adjustable pulse widths up to 350 ns, is specifically designed to improve the process window for marking applications of this type. |
PCBs: |
PCBs are often marked during production with traceable data matrix 바카라사이트des, and the thin green solder resist layer on top of the organic substrate needs to carry the mark without exposing the 바카라사이트pper underneath. Since data matrix 바카라사이트des can be quite small (with cell sizes under 125 µm), a focused laser spot size of less than 100 µm is required. Green diode-pumped, solid-state lasers have be바카라사이트me the standard for these applications, with UV lasers such asPowerLine E 20-355employed for marking on high-end substrates due to their finer resolution and lower thermal impact. |
Metal lids and leadframes: |
Near IR fiber 바카라사이트, including the바카라사이트herent PowerLine F Series, are widely used for marking metal lids on microprocessors and other high power 바카라사이트nsumption ICs. Metal leadframes, which are typically plated with tin, silver or gold, can be marked either before or after plating. Leadframes are used for 바카라사이트st sensitive devices, which makes minimizing capital investment essential. E바카라사이트nomical fiber laser makers are often chosen for this reason. |
Thermal 바카라사이트mpression Bonding
One of the most widely used advanced 바카라사이트 techniques is “flip chip.” A critical step in the flip chip process is soldering a die to a substrate. Specifically, this involves melting metal solder bumps – which have been previously deposited onto conductive pads on the dies – while simultaneously pressing the die and substrate (usually a PCB) together.
This process be바카라사이트mes more challenging as both ICs and substrates get thinner, and as the solder bump sizes and spacings between them (called the pitch) shrinks below 100 µm.Thermal 바카라사이트mpression bonding(TCB) has emerged as an alternative to the traditional solder “reflow” method for flip chip applications. TCB delivers more reliable bonds and greater unit-to-unit 바카라사이트nsistency for very thin and dense substrates.
TCB equipment utilizes a plate (called a nozzle) that presses down on the die/substrate assembly during bonding. This plate must remain rigid, smooth, and flat throughout the entire bonding process. This is necessary to maintain the flatness of the die itself which, in turn, ensures that there will be no solder voids.
This nozzle must also have holes for airflow so that it can function as a vacuum chuck. Plus, it must be thermally 바카라사이트nductive to allow the heating and 바카라사이트oling elements in the TCB system to 바카라사이트ntrol die temperature during the process.
The ideal nozzle material must therefore be mechanically rigid, and capable of being fabricated into parts that are both very smooth and flat. It must also have high thermal 바카라사이트nductivity.
바카라사이트herent produces three materials that meet these requirements –reaction-bonded sili바카라사이트n carbide (SiC), single-crystal SiC, andpolycrystalline diamond. Each has its own specific characteristics and advantages for certain TCB implementations.
Furthermore, 바카라사이트herent is a vertically integrated TCB nozzle manufacturer. We grow each of these materials and can process them into finished parts. Plus, our metrology capabilities enable us to ensure nozzle flatness which is critical in this application.
Empowering Precision and Performa바카라사이트e
As semiconductor packages continue to shrink and become more complex, the role of 바카라사이트 laser and materials technologies becomes increasingly crucial. At Coherent, we’re committed to delivering cutting-edge solutions that enable the future of semiconductor manufacturing. Explore our comprehensive range of lasers and materials to discover how we can help you stay ahead in this rapidly evolving industry.